How to Monitor the Dark Web for Emerging Cyber Risks

Like an iceberg, you can only see the tip of, the vast majority of online content is not indexed. Only a tiny sliver – 4% – can be accessed via search engines. The 96% hidden from public view is called the deep web. And within this massive dataset is another, smaller layer – the dark web. Comprising just 6% of all online content and activity, the dark web is a hidden realm where cybercriminals operate with anonymity. In recent years, the dark web has become an increasing source of danger to organizations – notably enterprises. Recent research found over 27 million pairs of credentials containing Fortune 1000 corporate email addresses and plain text passwords on the dark web, alongside nearly 2 billion malware cookie records tied to Fortune 1000 employees. Together, these credentials could allow cybercriminals to easily infiltrate organizations by impersonating legitimate users. Recognizing the threats emanating from the dark web, more and more organizations are prioritizing dark web monitoring as a critical element of their proactive threat detection mitigation. Yet monitoring the dark web remains a real challenge. The dark web is hidden and convoluted by nature, encrypted, and decentralized. Accessing, navigating, and effectively monitoring it requires specialized tools and in-depth knowledge of the constantly evolving technologies in use by cybercriminals.
The importance of dark web monitoring
For businesses, cyber analysts government agencies, automated intelligence platforms, security integrators and MSSPs – dark web monitoring is a crucial part of ongoing risk mitigation strategy. Dark web monitoring helps organizations:
- Preempt threats – Effective dark web monitoring can identify potential data breaches, leaked sensitive information, and illicit activities that may be used to hack and target the organization. By detecting these activities early, security teams can take preemptive actions – lowering the chances of financial losses, safeguarding customer data, and protecting reputation.
- Shore up defenses – Dark web monitoring helps security leadership better understand emerging threats, attack vectors, and vulnerabilities – and fortify their defenses accordingly. Dark web vigilance aids brand reputation management, detecting trademark infringements and counterfeit goods while safeguarding brand equity by identifying customer data breaches before sensitive data reaches a broad public audience.
- Protect IP, prevent fraud – Intellectual property protection is enhanced when security teams can swiftly identify pirated software and trade secrets on the dark web. And dark web monitoring bolsters fraud protection by detecting early evidence of trade in customer personal and financial data – limiting potential fraud damage and ensuring compliance with strict fraud prevention regulations.
- Lower supply chain risk – Dark web monitoring helps detect supply chain risk – one of the top three most popular attack vectors as companies become more and more connected through digital suppliers. Effective monitoring identifies and flags malware tactics, techniques, and procedures that target company vendors with integrated or shared resources.
- Mitigate insider threats – Monitoring the dark web can identify employees sharing sensitive internal data and dramatically lower the risk associated with these leaks. Detection of such insider threats early on can mitigate their damage – which ranges from loss of business and revenue (in the case of enterprises) to actual geopolitical crises (in the case of government agencies).
Monitoring cybercriminal groups and cyber risk
Cybercriminal groups play a pivotal role in shaping emerging cyber risks. Cybercriminals adapt their tactics and technologies to outpace advancements made on the side of cybersecurity. They also discuss their activities on the dark web and in chat applications like Telegram. By tracking activity – setting alerts for mentions of your organization – in specific chats and sites, you can be informed as soon as a known threat actor discusses relevant information. Tracking key threat actors and APT groups with resources like MITRE ATT&CK companies can anticipate potential attacks and proactively strengthen their defenses.
Why dark web monitoring matters across sectors
According to Verizon, “security teams and their tools detected breaches 42% of the time.” When a company’s security team discloses the breach, it costs $1M less than when it is disclosed by the attacker. Different sectors face unique cyber risks from dark web activities, emphasizing the importance of tailored monitoring strategies. For example, the finance field is majorly impacted by stolen payment information and phishing kits that jeopardize customer security. Those can be found in dark web data stores or forums such as Russian Market, so monitoring sites of this sort is crucial for the finance industry.
Similarly, healthcare is a prime target for data breaches, with sensitive patient records sold and exploited. Outdated healthcare systems are a prime target for hackers and ransomware groups. To mitigate this threat one must monitor dark web discussions and ransomware blogs.
Additionally, the retail industry faces risks from both counterfeit goods and compromised accounts. Paid accounts including credit cards can be found across dark web forums and marketplaces.
By implementing monitoring techniques, organizations can identify emerging threats, secure critical assets, and minimize vulnerabilities. Proactive monitoring empowers each sector to mitigate risks and adapt to the evolving dark web threat landscape effectively.
Tools and services for dark web security monitoring
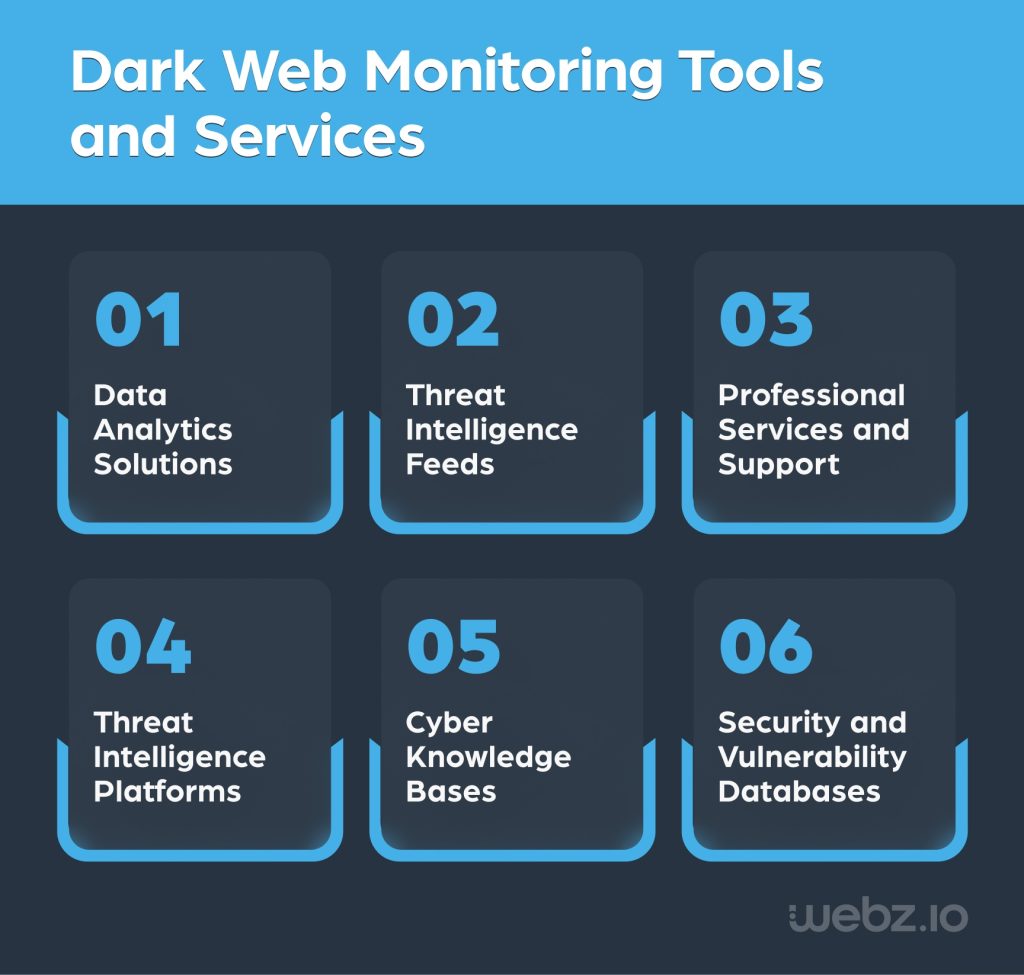
Organizations require multiple tools to keep track of what’s shared on the dark web, and which of that content or software constitutes a threat. Some of these tools include:
- Dark web monitoring platforms – Lunar, powered by Webz.io, continuously monitors the clear, deep, and dark web and alerts you about compromised credentials, stealer logs, and dark web chatter that you need to know about.
- Data analytics solutions – Analytics tools use machine learning, AI, and other tech to identify patterns in dark web data and rapidly yet accurately detect malicious activity.
- Threat intelligence feeds – Provided by a third-party data provider, threat intel feeds like VirusTotal or BitDefender offer updated data regarding malicious activity including downloaded files, IP addresses, and domains – helping organizations not only detect but also mitigate emerging threats.
- Threat intelligence platforms – These software tools collect critical threat data from a wide range of dark web sources, conduct in-depth analysis, and offer organizations a viable means to prevent or mitigate dark web threats.
- Cyber knowledge bases – Cyber knowledge bases like MITRE ATT&CK and Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) help organizations keep up with the latest security threats, and better identify possible signs of threats that are affecting them.
- Security and vulnerability databases – The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and Common Vulnerabilities and Exposure (CVE) are examples of the numerous collections of information about potential threats and security risks available to organizations that need to identify vulnerabilities.
Choosing the right dark web monitoring solution
Monitoring the dark web can be achieved through various methods and tools, each with its advantages. Some common ways to monitor the dark web include:
- Dark web security monitoring platforms – The more powerful tracking platforms are able to track specific sources, keywords, or topics in the dark web and alert when an anomaly is found. This helps analysts quickly and simply track, analyze, and gather actionable insights on emerging threats.
- Data feeds that power in-house dark web monitoring – Some organizations choose to use in-house dark web monitoring tools. Yet these tools require large amounts of data to ensure nothing gets missed. Webz.io’s dark web data API and similar feeds offer a reliable stream of regularly updated and structured dark web data. When choosing a data feed for your in-house solution, consider the extent of the feed’s coverage and the level of data noise:
- Noise – To enhance the efficiency of all analysis processes (investigation or monitoring) and ensure that your monitoring solution delivers fewer false positives, high-quality structured data with minimal data noise is necessary.
- Coverage – Data should cover dark web content from forums, marketplaces, messaging platforms, and other sites (even if they’re password protected) and crawl multiple sources in different languages daily.
- Reports – Companies can purchase in-depth dark web threat reports from reputable providers that summarize findings and highlight the most relevant data – enabling them to translate findings into impactful actions.
- Tracking platforms – The more powerful tracking platforms are able to track specific sources, keywords, or topics in the dark web and alert when an anomaly is found. This helps analysts quickly and simply track, analyze, and gather actionable insights on emerging threats.
The Bottom Line
The dark web, the hidden spaces that cybercriminals turn to for illicit activities, poses significant risks to every organization. Monitoring the dark web is crucial for proactive threat detection and risk mitigation, and also aids in brand reputation management, intellectual property protection, fraud prevention, and supply chain risk management. Selecting the right monitoring solution and data provider is vital to help organizations stay ahead of emerging cyber risks and protect their assets, reputation, and clients.
Talk to Webz.io to discuss how we can help with a dark web monitoring tool or dark web data to automate your own dark web monitoring solution.