The Top Supply Chain Risks on the Dark Web

In today’s interconnected and globalized business landscape, supply chain risk management (SCRM) has become critical for organizations across all industries. From large multinational corporations to small businesses, the reliance on complex supply networks has exposed companies to many different risks.
While supply chain risk and disruptions can arise from various sources, such as natural disasters, or unexpected pandemics, in this article we’ll focus on the cyber threats which make up a huge portion of all supply chain disruptions around the world.
What is supply chain risk?
Supply chain risk consists of a wide variety of potential threats that stem from a company’s reliance on third parties. These can pose a risk to other entities within the same supply chain. When it comes to cybercrime, supply chain risks include different threats such as data breaches, vulnerabilities, malware, or any other cyber threat that help malicious actors access and compromise data or any digital system within the supply chain.
Who should worry about supply chain risks?
Supply chain disruptions can have a far-reaching impact on all businesses. Cyber attacks against supply chains can lead to severe operational disruptions, leading to serious damages such as data loss, financial losses, and reputation damage followed by customer dissatisfaction. Because of the ever-evolving risk landscape and the rise in the number of supply chain attacks, businesses need to proactively identify and mitigate any threat to protect their operations and eventually – their bottom line.
One of the most important places to collect critical intelligence and stay ahead of those threats is the deep and dark web. Most cybercriminals use these platforms to discuss and plan their attacks, making these spaces critical sources for monitoring supply chain risks on a daily basis. Later in this article, we’ll discuss how this can be done, but let’s first take a look at the type of supply chain risks you can find on the deep and dark web.
What types of supply chain risks can be found on the deep and dark web?
Data Breaches
The deep and dark web is a central hub for stolen or leaked data. This type of data can include customer information, login credentials, and sensitive business information. This stolen data can be exploited to compromise supply chain partners, gain unauthorized access to systems, or carry out targeted attacks such as ransomware attacks, IoT attacks, credential stuffing, or phishing attacks.
Let’s take a look at the following example.
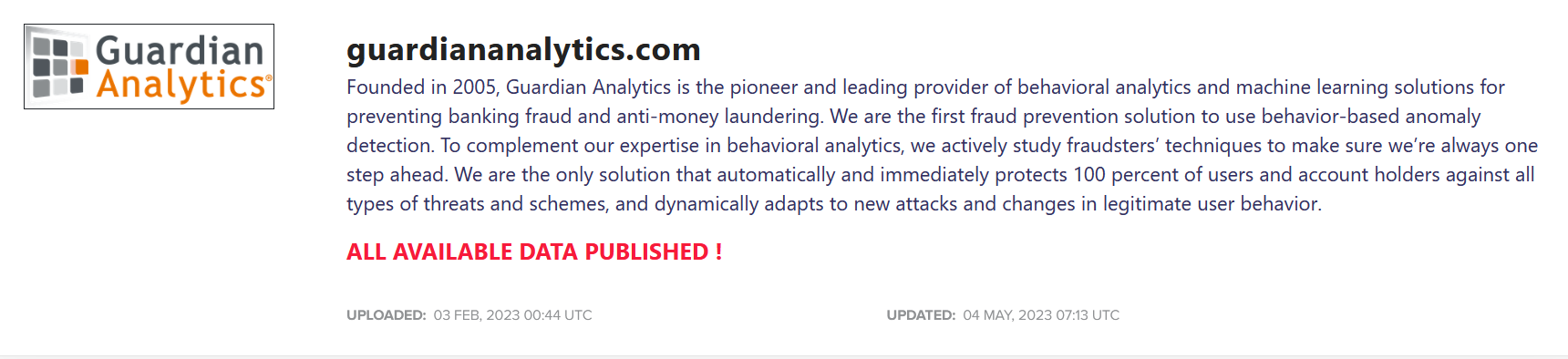
Guardian Analytics, an American business now under the name of Nice Actimize, was attacked by “Daixin Team”, a ransomware and data extortion group. After what seems like the company’s decision to decline the ransomware demands, the group leaked internal information it stole from the company in January 2023, on the site the group maintains on the Tor encrypted network.

A few weeks later, in February, this company was attacked again by another known ransomware group called “Lockbit”. There is a high chance that there is a connection between the two since leaked data assists threat actors to gain unauthorized access to the company’s system from a different attack vector.
The following image was taken from Loclbit’s Tor website offering a link to download the data they stole from Guarding Analytics.
In the aftermath of these data security incidents, Webster Bank, a Guardian Analytics vendor, reported being adversely affected when unauthorized third parties gained access to files containing the personal information of Webster clients from Guardian’s systems.
The files that were stolen were subsequently posted online, as stated in a letter sent by Webster Bank to the Massachusetts Office of Consumer Affairs and Business Regulations. The incident has already affected Webster Bank as it has raised concerns regarding the security and privacy of their clients’ information.
Zero-day exploits
Zero-day exploits are vulnerabilities in software or systems that are unknown to the vendor, which means the vendor does not have a patch available. When cybercriminals find zero-days but do not intend to use them to launch an attack themselves, they advertise them on the deep and dark web, knowing there’s high demand for them and the price is steep. Zero-days can be easily used by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to the supply chain system, given the fact they aren’t patched yet. Once used, the zero-days enable hackers to access sensitive information and even manipulate it.
In the following post, published recently on OnniForums, a threat actor is offering a zero-day vulnerability he found in MyBB’s system, a free and open-source forum software, which according to the company is used by over 235 companies around the world.
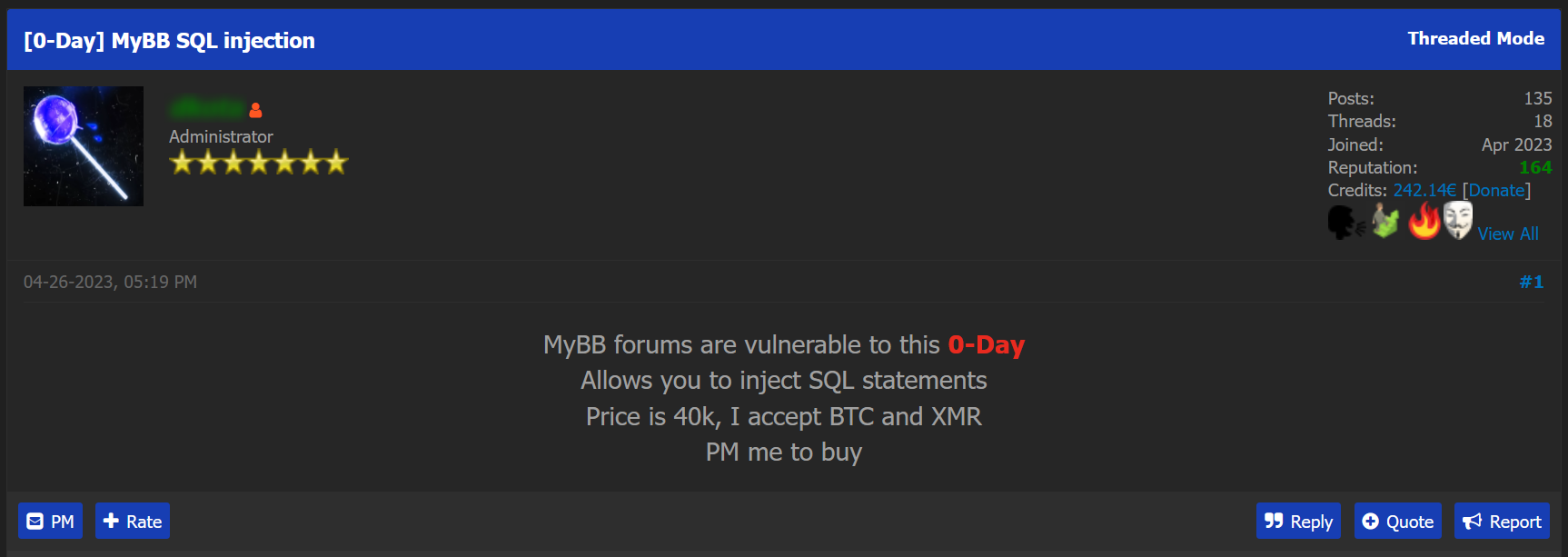
The zero-day offered for sale in the post allows attackers to inject malicious SQL code into any MyBB forums, which can potentially bypass security controls, access or modify the database, extract sensitive information, or perform unauthorized actions within the affected system.
This is a classic example of how a threat against a certain supplier can affect another multiplier in the same chain.
Malware trade and malware attacks
Illegal trade is the most widespread activity of cybercriminals on the deep and dark web. One of the most popular commodities traded is malware, so popular that many platforms have dedicated sections just for malware sales and discussions.
Malicious actors may discuss, share or sell ready-to-use malware tools and even offer malware-as-as-service. Malware-based attacks can pose a serious risk to supply chains given the fact that it has the capacity to manipulate essential computing operations, track computer activities without the admin’s knowledge and steal internal data stored in the system.
In the following post, published on the underground forum Dread, a threat actor says he is planning to carry out a malware attack against an ATM manufactured by Wincor Nixdorf using Ploutus (ATM Malware) in order to dispense cash:
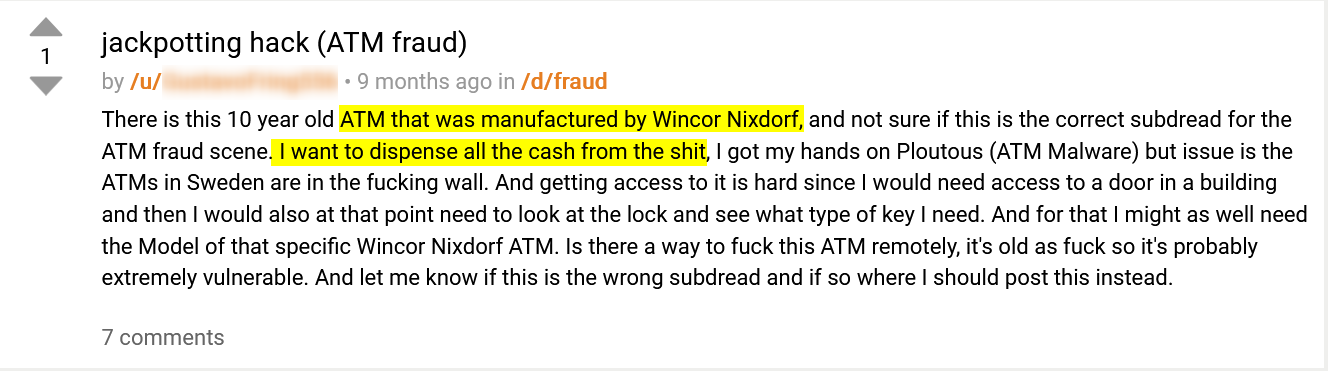
This is another good example of a supply chain risk banks are facing.
How can deep and dark web monitoring help prevent and mitigate supply chain risks?
Monitoring the dark web plays a crucial role in monitoring supply chain and third-party risks as it enables companies to access the prime source of cybercriminal activity. Over the past years, the dark web has become known for hosting underground forums and marketplaces where stolen data, compromised credentials, and hacking tools are traded.
By monitoring the dark web, businesses can proactively identify if their suppliers’ or customers’ sensitive information or intellectual property is leaked or sold, and by that prevent or mitigate potential cyberattacks against their own systems. Monitoring the dark web allows companies to also stay ahead of emerging cyber threats, such as zero-day exploits or new malware, which can be used against their supply chains.
This is why the largest dark web monitoring platforms are using Webz.io’s dark web data feeds to monitor the dark web. It helps them gain direct access to the largest repository of deep and dark web data, keeping them ahead of emerging threats to their supply chain.