How to Automate Supply Chain Risk Reports: A Guide for Developers
Do you use Python? If so, this guide will help you automate supply chain risk reports using AI Chat GPT and our News API.

Data loss has a lasting effect on the future of organizations. In the aftermath of an attack, organizations lose data that will need to be changed or retrieved and often lose money and customers. Most organizations will need months and sometimes years to repair the reputational damage they suffered from such an attack.
We examined reports from IBM, Ponemon Institute, and Verizon to identify the industries that are the most likely to suffer from a data leak.
Several industries stand out as particularly high-risk for data leaks, including healthcare, financial services, technology (including information technology), retail, and the public sector (including education and government). The majority of threat actors targeted all sectors for financial gain. In the case of technology companies, 14% of data leaks were motivated by espionage.
| Industry | Incidents in 2024 | Top Attack Patterns | Type of Data Disclosed |
| Healthcare | 1,378 | Miscellaneous Errors, Privilege Misuse, and System Intrusion | Personal, Internal, Credentials |
| Financial Services | 3,348 | System Intrusion, Miscellaneous Errors, and Social Engineering | Personal, Bank, Credentials |
| Technology | 1,367 | System Intrusion, Basic Web Application Attacks, and Social Engineering | Personal, Credentials, Internal |
| Retail | 725 | System Intrusion, Social Engineering and Basic Web Application Attacks |
Credentials, Other, Payment, System |
| Public Sector (including Education) | 1,780 | System Intrusion, Social Engineering | Personal, Internal, Credentials |
The healthcare sector remains a top target for cybercriminals due to its critical role in public health and the sensitive nature of the personal health information (PHI) it manages. Patient records, billing data, and other health-related information make healthcare organizations prime targets for ransomware attacks, social engineering, and data theft. Data breaches affected between 500 and 1.8 million individuals per incident.
In 2024, cyberattacks targeting healthcare organizations involving ransomware and data theft were the most significant threats. Outdated systems and insufficient cybersecurity measures leave healthcare organizations at a heightened risk for data breaches that not only affect PII but could also disrupt operations and patient care.
Insufficient cybersecurity resources and outdated medical devices make healthcare extra vulnerable to cyberattacks.
In 2024, Change Healthcare, a payment processor for the healthcare industry, was breached, affecting UnitedHealth’s platform. UnitedHealth linked the breach to ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware group. It involved encrypting operational systems and exfiltrating large amounts of sensitive data, including personal and medical information, as well as financial data. Exposing data from Change Healthcare on the dark web had significant ramifications across the U.S. healthcare system, causing major disruptions in billing and payment processes and delaying patient care. Change Healthcare, which processes millions of transactions annually, serves numerous hospitals, clinics, and medical facilities. As a result, the breach affected a wide array of healthcare organizations, showcasing how an attack on a single platform can ripple through the entire industry.
Since financial institutions manage sensitive personal and banking data as well as have direct access to monetary assets, they are a frequent target for cyberattacks. Credential theft, phishing, and ransomware dominate as the most prevalent threats, with financial institutions in 2024 experiencing a sharp increase in spear-phishing campaigns and supply chain attacks. According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach in this industry is $6.08 million per incident.
A notable data breach in the financial sector happened in November 2024. Unauthorized access to Finastra’s Secure File Transfer Platform (SFTP) exposed sensitive data from some of the world’s largest banks on the dark web.
We used Lunar, our dark web monitoring platform to look for examples of stealer logs from the recent Finastra data breach. Below is an example of a stealer log for sale on a dark web marketplace called Russian Market. Stealer logs containing compromised credentials like usernames, passwords, and session cookies, enable attackers to bypass authentication measures and directly access banking systems or sensitive customer data.
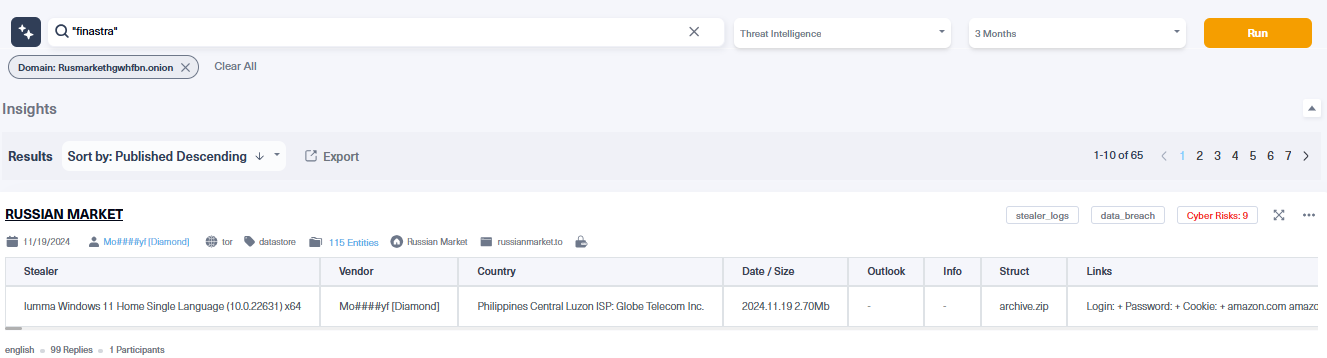
This combination of real-world breaches and dark web activity underscores the growing sophistication of cyberattacks targeting the financial sector. Institutions must prioritize robust measures, including:
Fast and efficient cyber threat intelligence is crucial to protecting data from the financial services sector. Webz.io partners with leading cyber intelligence and event monitoring companies to provide enriched deep and dark web data. Dark web intelligence enables organizations to track indicators of compromise (IOCs), detect high-risk signals like those found in the screenshot above, and proactively defend against emerging threats.
The technology industry, particularly information technology, faces significant cybersecurity risks due to its handling of valuable data and expansive digital infrastructure. This sector is often targeted by sophisticated cyberattacks, including system intrusions and the exploitation of vulnerabilities in critical systems. Companies that provide solutions for storing, manipulating, and analyzing data become prime targets for breaches because they have access to large amounts of data.
Over the past few years, the number of supply chain attacks has increased. Threat actors exploit trusted third-party vendors to gain unauthorized access to data and systems. These attacks highlight the need for robust cybersecurity measures in B2B technology solutions, as they not only put corporate assets at risk but also endanger client data.
The retail industry is at risk due to the large amount of consumer data it collects and processes. Common attack vectors include point-of-sale (POS) intrusions, web application attacks, and credential theft, all aimed at financial fraud or data breaches. The sector’s extensive digital footprint—spanning cloud services, backups, and admin-level access points—creates multiple attack surfaces for cybercriminals.
One cause of data breaches in the retail industry is low-security standards. Retailers rely on third-party organizations to provide security services, and some have little to no security measures at all. Attackers know this and exploit the weaknesses of the retail sector through methods like phishing, DDoS attacks, and ransomware, often after extensive intelligence gathering.
Among the most common attack methods, you can find phishing sites. There are also different types of DDoS attacks and some ransomware attacks, which are used as part of a more sophisticated attack that is customized per organization after a long process of intelligence-gathering by the threat actor. Some data breaches that affect department store chains result in leaking customers’ online accounts, credit card numbers (with expiration dates), and passwords.
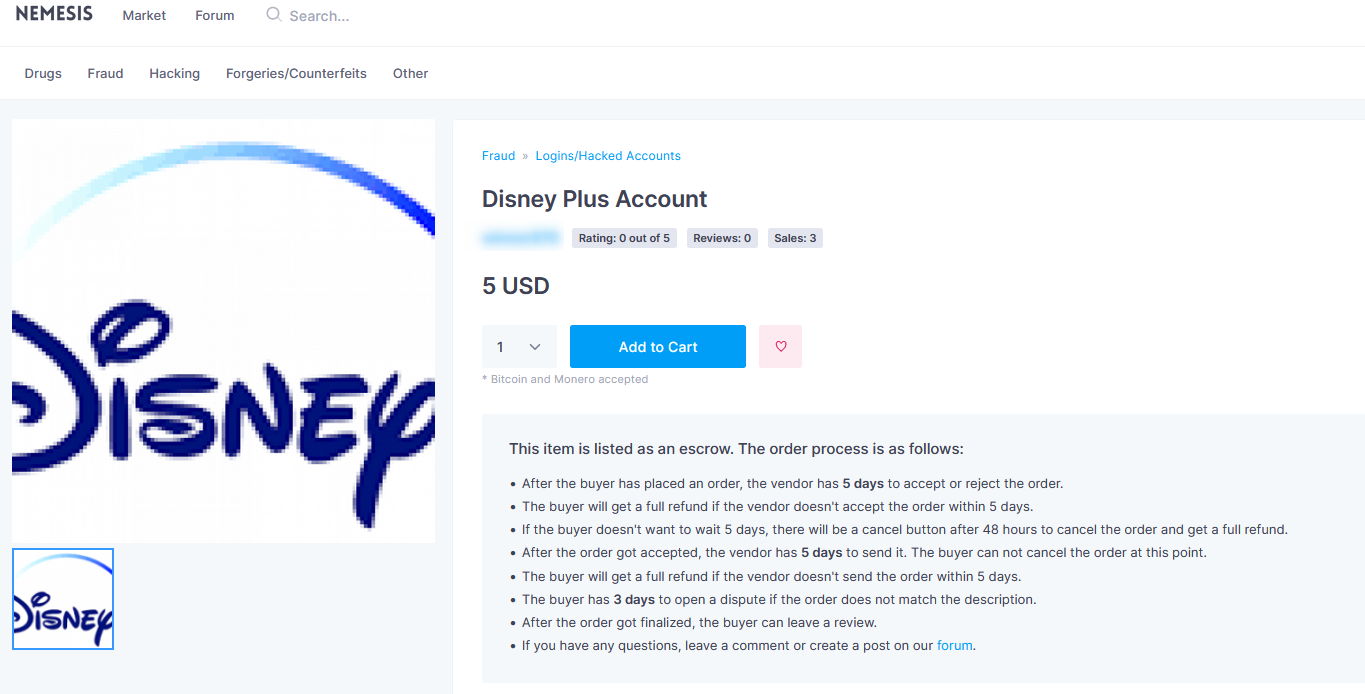
For example, following a breach, Disney accounts were found for sale on the dark web. These accounts, often containing sensitive data such as gift card information, allow attackers to commit financial fraud and potentially leak further personal details, escalating the risk of additional attacks. Tens of thousands of such accounts are trafficked daily, underscoring the growing threat to retailers.
The public sector includes government agencies and educational institutes. Government agencies are at risk, primarily due to espionage motives alongside typical financial motivations. Attackers often target vulnerabilities in public-facing applications and email phishing campaigns, causing service outages that compromise not only sensitive data but also the continuity of essential services.
Educational institutions are a treasure trove of personal information, research data, and financial details, making them a target for ransomware attacks and data breaches. They often have feebler security systems than other high-risk industries.
High-risk industries must adapt their security strategies to stay ahead of cyber attacks as cyber threats evolve. Integrating AI and automation into cyber threat intelligence tools is a powerful way to mitigate the risks of data leaks and make sure your organization is the first to find compromised relevant credentials on the dark web.
By embracing these emerging technologies and best practices, organizations in high-risk industries can significantly reduce their exposure to data breaches and safeguard their sensitive information.
Is your organization in one of these fields? Learn how to monitor the dark web to protect your company from costly breaches using Lunar by Webz.io

Do you use Python? If so, this guide will help you automate supply chain risk reports using AI Chat GPT and our News API.

Use this guide to learn how to easily automate supply chain risk reports with Chat GPT and news data.

A quick guide for developers to automate mergers and acquisitions reports with Python and AI. Learn to fetch data, analyze content, and generate reports automatically.