How to Automate Supply Chain Risk Reports: A Guide for Developers
Do you use Python? If so, this guide will help you automate supply chain risk reports using AI Chat GPT and our News API.

A paste site is a website that allows users to store and share text-based information, such as code snippets, scripts, configuration files, or any other form of plain text. Paste sites typically provide users with a simple interface to paste their content. The content is then saved as a unique URL that can be shared with others. There are thousands of paste sites online, most of which cater to specific groups of interests.
Paste sites are commonly used by developers, system administrators, and other technical professionals for sharing code snippets and troubleshooting. However, their anonymity features make them attractive to cybercriminals for sharing sensitive information and malicious content.
The popularity of paste sites among threat actors and cyber criminals can be attributed to several factors related to the nature of the websites and how they can be used for malicious activities.
The majority of the paste sites are found on the open web, but some can also be found on encrypted networks. Since these sites offer their users a level of anonymity when sharing pastes, users are likely to be less concerned about whether the paste site operates over an encrypted or open web platform and are more likely to decide which paste site to use according to the main topics found on it.
Most paste sites keep a database of all their historical ‘paste files’ accessible to the public. Those which are published on open websites in particular can be even more easily accessible, since they can be indexed by standard web search engines, such as Google or Bing.
However, some paste files are more restricted to the public. Because several paste sites allow their users to hide their files, only people with a unique URL can get full access to them. The reason for this is to allow anonymity to users who wish to remain anonymous or keep their files more protected.
We used Lunar, our deep and dark web monitoring platform, to find the leading paste sites used by cybercriminals. We have listed them from the site most used to the least used:

Paste sites have become a popular platform for cybercriminals to distribute illegal content, due to their simplicity, anonymity, and limited moderation. The types of illegal content commonly found on these sites can vary, but the following are some of the most prevalent and concerning:
Paste sites play an important role in the world of cybercrime as they work hand in hand with chat apps and the dark web, making it easier for criminals to share stolen information and coordinate their activities efficiently.
As mentioned before, some of the content on paste sites is illicit. We used our Dark Web API to find three examples of pastes that feature leaked stolen data, hacking tools, and a cybercriminal service listing. By understanding the diverse range of illicit content on paste sites and the potential impact of these activities, organizations and individuals can take steps to protect themselves from cyber threats.
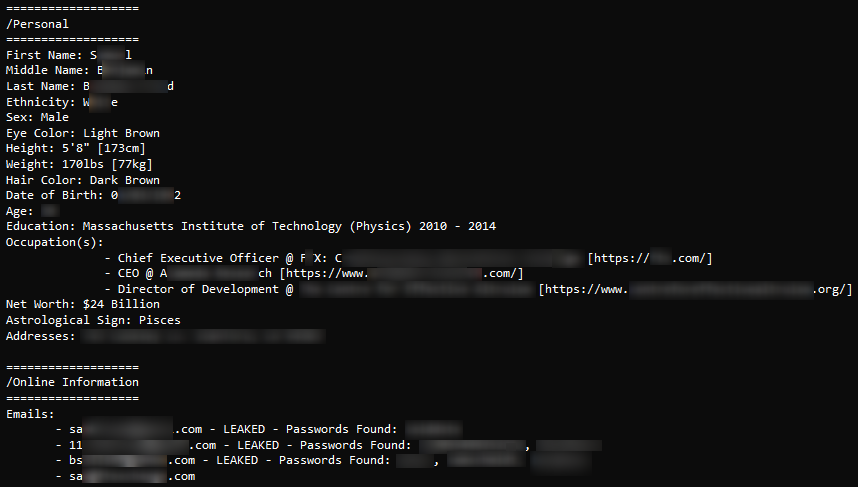
The following post, which was published on the well-known paste site DoxBin, features private data from several executives. The data includes email addresses, phone numbers, social media profiles, education, occupation, physical addresses, birth dates, etc. DoxBin paste site is known as an important source of information belonging to and targeting executives and VIPs.
This type of sensitive information can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage.as published on the known paste site DoxBin, features private data of several executives.
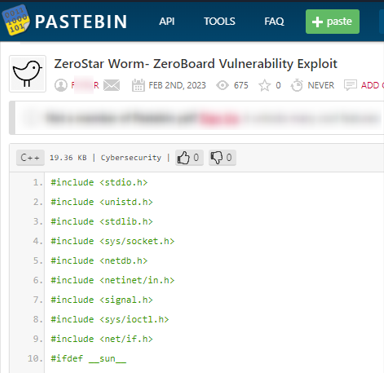
Example #2: Hacking tools
Threat actors frequently use paste sites to share and store malicious scripts, exploit kits, and other hacking tools. These tools can be used to launch large-scale cyberattacks, targeting critical infrastructure, businesses, and individuals.
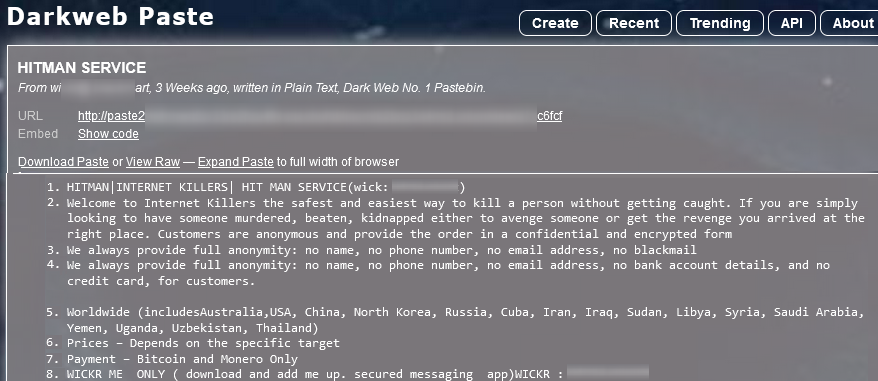
Below is an example of a post from Darkweb Paste, a Tor-based hidden platform, offering hitman services, which are typical to paste sites:
Monitoring paste sites has become essential for protecting organizations from a range of cyber threats. Paste sites, while often publicly accessible, can also feature hidden or restricted posts, some of which may only be available on the dark web. These sites are commonly used by cybercriminals to share sensitive and illegal content, such as stolen data, hacking tools, and exploit scripts. Since many paste sites are minimally moderated, harmful content often remains online long enough to be widely distributed, increasing the risk of data breaches or other attacks. By actively monitoring these platforms, organizations can uncover vital threat intelligence—such as emerging vulnerabilities or data breaches—that may not be visible through typical web searches, allowing them to act proactively to protect their sensitive information.

Do you use Python? If so, this guide will help you automate supply chain risk reports using AI Chat GPT and our News API.

Use this guide to learn how to easily automate supply chain risk reports with Chat GPT and news data.

A quick guide for developers to automate mergers and acquisitions reports with Python and AI. Learn to fetch data, analyze content, and generate reports automatically.